
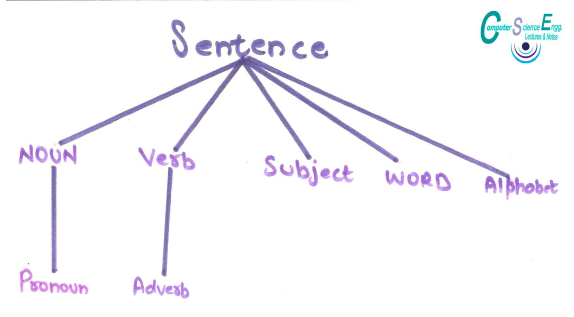
Formal Methods of Describing Syntax
English:
Alphabet: a,b,c,d,e,f,,,,z,A,B,C,....Z.
Punctuations:,.''!""_/
I eat chocolate- Words: Combination of alphabets

Sentence:
Eat I. Chocolate*
 He eat chocolate- words are correct
He eat chocolate- words are correct
 He eat chocolate.*
He eat chocolate.*
 Here eat should be eats by Tenses
Here eat should be eats by Tenses
 Sentence:
Sentence:

Programming language
1. Alphabets: a,b,c,d,-----z,A,B.....Z
2. Digits: 0,1,2,3....9
3. Arithmetic symbol: *,-,/,+
4. Special symbols: ->.....#,@,!

Programming language in more technical way
header file: Math.h
statements : Tokens
Expression: Lexemes
Identifiers: Literals
These all need a grammar which can describe their syntax.
Grammar: Syntax and structure of a language. It is used in compiler creation. Describe the syntax of a programming language.
Natural Language: A language that has developed naturally through use.
Artificial Language: Language used to communicate with computers.
Syntax: The rules governing the arrangement of words and phrases to create well formed sentences .
Meta language:
• Language used to model the other language.
• Determine whether a series of characters is valid.
• Generate girlfriend statement.
• Breakdown a statement into constituent parts so it can be converted into Machine Language.
Token: Each and every smallest individuals units in programming language are known as token.
c tokens are of six types
| Type | Example |
|---|---|
| Keywords | int , while |
| Identifier | Main, total |
| Constants | 10, 20 |
| Strings | " total"," hello" |
| Special symbols | (),{} |
| Operator | +,*,-,/ |
Example
int main()
{
int x,y,total;
x=10,y=20;
total=x+y;
printf(" total=%d\n", total);
}
Where
| main | identifier |
| {,},(,) | delimiter special control |
| int | keyword |
| x,y,total | identifier |
| Man,{,},),(,int,x,y,total | tokens |

