
Static and Dynamic Data Structure
Static Data Structure:
Static Data Structure means set of data, but that does not mean that we cannot change the assigned value of elements.
• Here static means the size of data type is fixed.
• Memory size allocated to 'data' is fixed.
Example:
int a[5]={ 1,2,3,4,5};
Here array [5] which has a fixed size in memory.
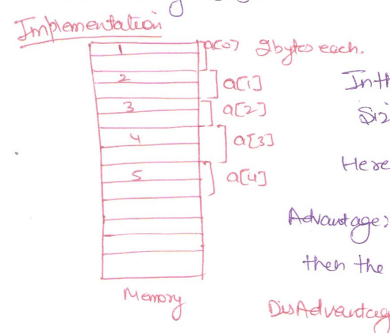
In this we cannot increase the size of Array at run-time. and Here size of 10 byte is fixed.
Advantage: Where we know the size of element of array to be used then the wastage of memory can we stopped.
Disadvantage: If we do not know the how much element to be used when it causes wastage of memory.
Dynamic data structure:
There are many situation where the number of items to be stored is not known before hand. In this case we use dynamic data structure.
• Data Structure is allowed to grow and shrink as the demand for storage arises.
• Programmer should set a maximum size of data to help avoid memory collision.
Disadvantage- Because the memory allocation is dynamic, it is possible for the structure to overflow, should it exceeds its allowed limit. For empty -It should maybe underflow and and it is quite harder to program.
Example
Stacks: In this elements can be added or removed at run-time.
02- What Is Difference Between Static And Dynamic Data Structure In C Programming Language
CLICK HERE TO Download This PDF NOTES
