
Data Definition Languages- integrity constraints, Referential Integrity, Authorization, Assertion
Different type of constriants in DDL:
Domain Constraint,
Referential Integrity,
Assertion,
Authorization.
Domain Constraint:
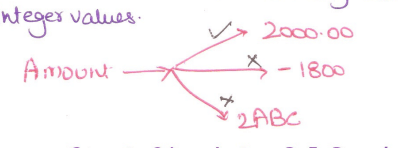
It specifies the set of possible values that may be associated with an attribute.Example like amount attribute it will only take positive and integer values.
Referential integrity:
Value that appears in one relation for a given set of attributes also appears in a other set of attribute in another relation. Example there are two tables called EmpDetail and EmpSalary. Table EmpDetail has attributes like Emp_Id Emp_Name and Emp_Salary: This table has attribute Emp_Id and Emp_Salary, Emp_Month and we have made Emp_Id referential to the table Emp_Salary's Attribute EmpId, then values in EmpId of table EmpDetail should match today EmpId of EmpSalary.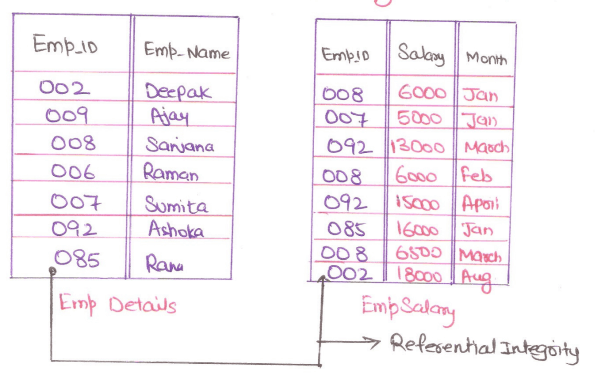
So EmpId of EmpSalary can only have values fromEmpId of EmpDetails.
Referential Integrity is implemented with the foreign key.
Assertions:
It is any condition that the database must always satisfy.For example: A table of student has attributes Marks, Name as the maximum marks is 100 so there will be an assertion on marks is that value in it cannot be -ve and more than 100.
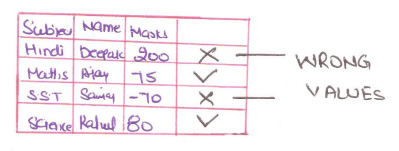 Value cannot be>100 7 -ve so we have to apply assertion on it.
Value cannot be>100 7 -ve so we have to apply assertion on it.
****Domain constraint and referential integrity are special form of Assertion.
Authorization:
Authorization means permission.
In DBMS, different authorisation are applied according to the user and the different authorisations are
Read Authorisation: In this only reading from the database can be done. We cannot modify anything in the table or in the database.
Insert Authorisation: In this authorisation we can only insert the data which should be new and we can't do anything else on database or in table.
Update Authorisation: In this authorisation we are allowed only to update or modify the data. We even can't delete any data in this.
Delete Authorisation: This authorisation only deletion in a table and we do not do anything else.

