Reduction of ER Diagram to Tables
For converting strong entity type there are some points that should be kept in mind.
• Entity type becomes a table in it.
• A Single - Valued Attribute becomes a column for a table.
• Derived Attribute are ignored and not considered in table.
• Composite Attribute are represented by components
• Multivalued Attributes are represented by Separate table.
• A key attribute of the Entity type becomes the Primary Key of the table.
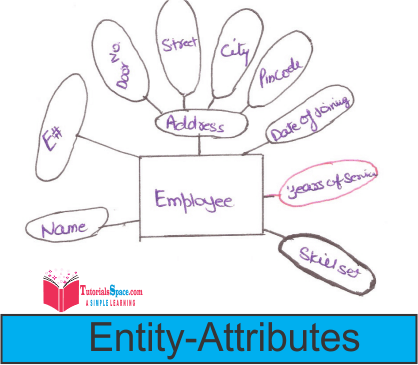
Example
• Here Address is Composite Attribute.
• Years-Of-Service is DSerived Attribute
• Skillset is a Multivalued Attribute : We have to make separate table but remember there should be relationship between an employee table and skill set table.
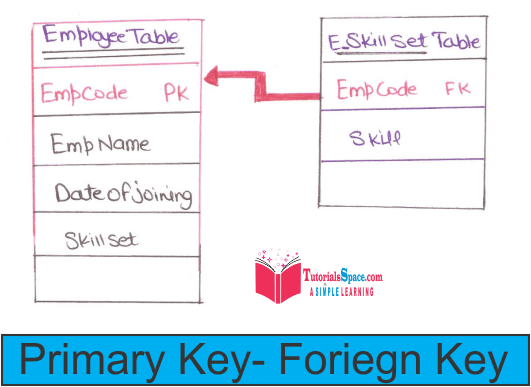
So the Relational Schema and Employee Skill set table is:>
Employee(E#, Name, Door_No,Street, city, pincode, date_of_joining)
Employeeskillset(E#, Skill)

As we saw E# has to be primary key for employee table hey uniquely identify an entity and employee skill set has skill which came from skill set (multi valued).
So to create a relationship between these two table we use E# i.e Employee Code in EmployeeSkill set table as a "foreign key" which implements Referential Integrity.
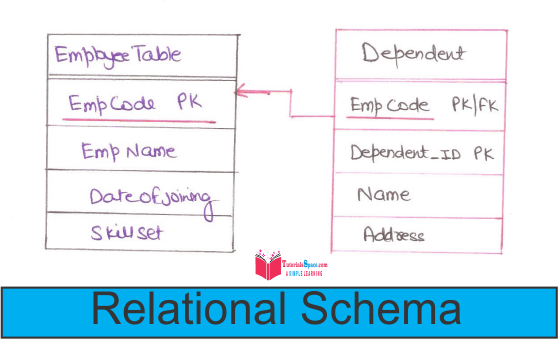
Converting Weak Entity Types:
• Weak Entity type are converted into table of their own, with the primary key of the strong entity acting as a foreign key in the table.
• This ForeignKey along with the key of the weak entity from the composite primary key of this table.
• The Relational Schema:
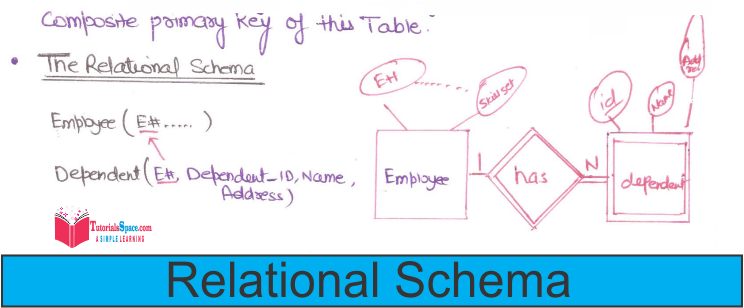
Employee(E#......)
Dependent(E#, Dependent_ID,Name, Address)