
04- Store Program Control Concept- General Purpose Computer System
CLICK HERE TO Download This PDF NOTES
"The Modified Von-NeuMann Architecture"
"Adding A SYSTEM BUS"
"Todays General computer System"
It is a basically modern day architecture representative
• The Processor Subsytem (i.e the CPU) now consists of the ALU and control unit and various processor registers.
• The processor, memory and I/O subsystems are interconnected by the system bus, which consists of data, address and control-status lines.
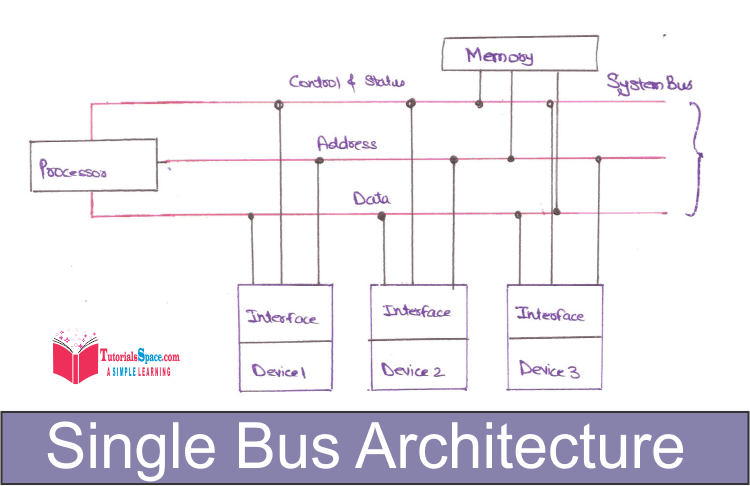
Practical systems may differ from the single bus architecture in sense that it may be configured round Multiple Buses.
For instance, there may be a memory bus that connects the processor to memory subsystem and an I/O bus to Interface I/O devices to the processor, forming a two-bus structure.
Further:- It is possible to configure a system with several I/O buses where in each bus may interface one type of I/O device to the processor.
Since Multiple Bus structures allow simultaneous operations on the buses, a higher throughput is possible , compared to single bus architecture.
However, because of the multi-buses the system complexity increases. Thus , a speed/Cost trade off is required to decide on the system architecture or structure.